Francesco M. Labricciosa, MD, Specialist in Hygiene and Preventive Medicine
Recommending a bundle with evidence-based measures for surgical antibiotic prophylaxis (SAP), easily applicable and helpful to improve antibiotic prescribing practices among surgeons worldwide. This is the aim of a narrative review just published in Antibiotics by Massimo Sartelli and colleagues.
Surgical site infections (SSIs) represent the most common healthcare-associated infections occurring in surgical patients. Therefore, all procedures aiming to prevent SSIs should be integrated before, during, and after surgery.
SAP is one of the most important measures to prevent SSIs. Nevertheless, many surgeons erroneously believe that SAP is peripheral to their clinical practice. But actually, surgeons play a central role in prevention SSIs.
Indeed, approximately 15% of all antibiotics in hospitals are prescribed for SAP. Using antibiotics appropriately, both for therapy and prophylaxis, is essential to improve treatment effectiveness and patient safety, reduce the risk of antibiotic-associated infections (e.g., Clostridioides difficile infection), and the selection and spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Several guidelines have been published regarding SSIs prevention, but measures stated in these guidelines are not self-implementing. Bundles are among the most used methods to adapt guidelines in local contexts, and improve acceptance and adherence to best practices.
As observed by the authors, bundles implemented as stand-alone interventions or as part of multimodal strategies were associated with decreased SSI rates.
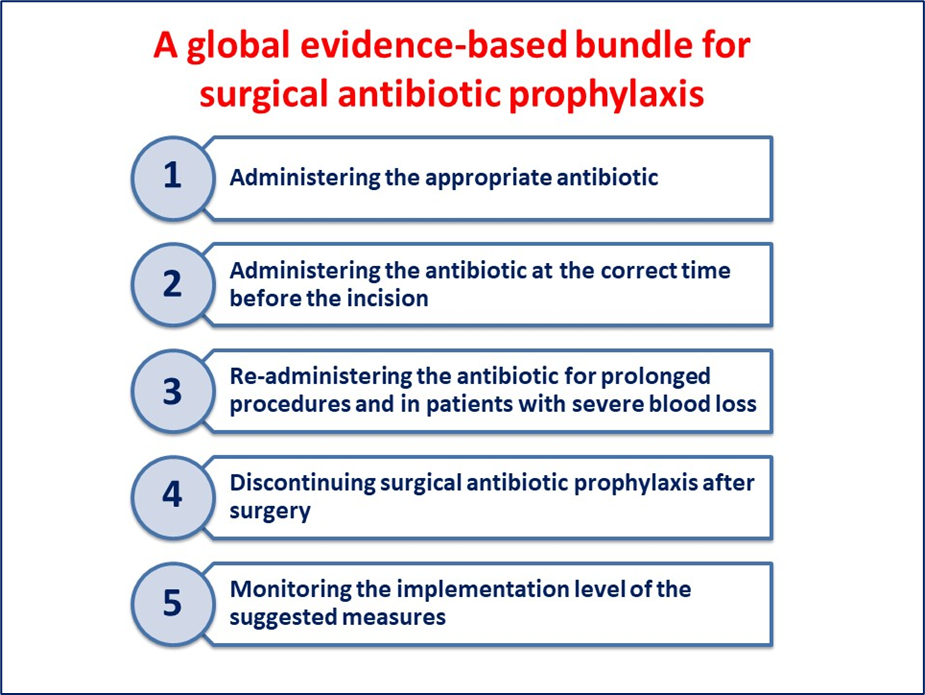
For these reasons, an international working group of 30 physicians has been established by the Global Alliance for Infections in Surgery. The authors aimed to define a global evidence-based bundle for the appropriate SAP administration, and evaluated the evidence supporting it.
This bundle includes five different actions that may affect adequate SAP administration.
In administering antibiotics for any indication, including for SAP, surgeons should always be responsible for handling antibiotics with care. Indeed, inappropriate prescriptions of these precious medications, as well as poor implementation of infection prevention and control measures, are contributing to the development and spread of bacterial antimicrobial-resistance.
The authors hope this bundle can be easily applied everywhere, and help to improve antibiotic prescribing practices among surgeons worldwide.
Reference
