Francesco M. Labricciosa, MD, Specialist in Hygiene and Preventive Medicine

Surgical site infections (SSIs) are among the most common healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and represent a major cause of postoperative morbidity, mortality, prolonged hospitalisation, and increased healthcare costs worldwide. Closely linked to antimicrobial resistance (AMR), SSIs remain a critical patient safety issue despite the availability of robust evidence-based prevention strategies.
The persistent gap between evidence and clinical practice highlights the need to prioritise effective implementation rather than the development of new preventive measures.
SSI prevention is embedded within comprehensive infection prevention and control (IPC) programmes, which are multidisciplinary and influenced by cultural, organizational, environmental, and patient-related factors.
Healthcare workers’ knowledge, awareness, and attitudes are central to translating recommendations into daily practice, while strong leadership, governance, adequate staffing, and continuous education provide the organizational foundation for IPC effectiveness. Environmental hygiene and patient vulnerability further influence infection risk, and increasing emphasis is placed on patient engagement as an active component of prevention.
International bodies such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), and professional surgical societies have issued comprehensive SSI prevention guidelines. However, adherence remains inconsistent across healthcare settings.
Evidence from implementation science shows that multimodal strategies, combining education, audit and feedback, standardized protocols, reminders, and performance monitoring are more effective than isolated interventions in improving compliance and reducing SSI rates.
To address these challenges, the Italian Multidisciplinary Society for the Prevention of Healthcare-Associated Infections (SIMPIOS) proposes a multimodal, continuous improvement framework aligned with the WHO implementation cycle. The paper has been recently published in Infection and Drug Resistance.
This framework conceptualizes SSI prevention as an iterative process that includes preparation and governance, baseline assessment and action planning, contextual adaptation of evidence-based practices, promotion of safety culture and behavioral change, and continuous evaluation through surveillance and feedback.
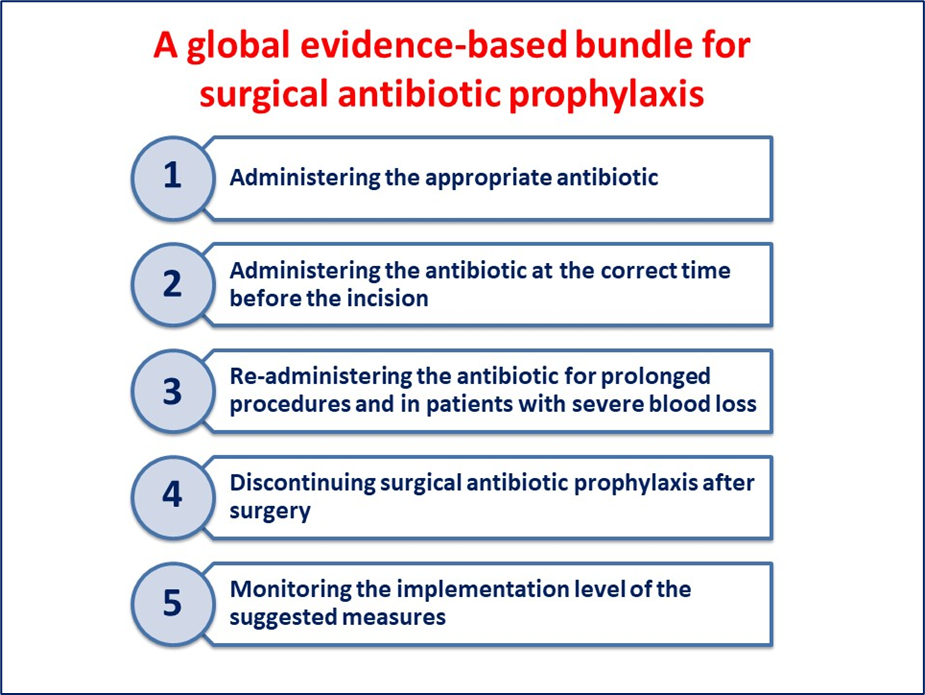
Practical implementation tools such as locally adapted protocols, care bundles, checklists, and visual reminders support the translation of guidelines into routine clinical practice. SSI prevention bundles, composed of a limited number of high-evidence perioperative interventions, have demonstrated significant reductions in infection rates when applied consistently.
Sustainable SSI prevention depends on a strong safety culture characterized by leadership engagement, interdisciplinary collaboration, psychological safety, and shared accountability. Surveillance systems, supported by audit and feedback, enable data-driven improvement, while emerging automated surveillance technologies may further strengthen IPC capacity.
Finally, a multimodal, continuous improvement approach provides a sustainable pathway for reducing SSIs and improving surgical safety, with principles applicable to the prevention of all HAIs.
Reference